Version Control¶
The version control allows to export or import a selectable number of nodes or the entire project. The exported data is mapped to text files on the file system and can be easily integrated into version control systems.
Hint
The version control is meant for archiving and tracking states of the project during development. It is not designed for the use in a running system, since it may result in undefinable system states.
The performance can be significantly improved by adding atvise applications (atbuilder.exe, atserver.exe, etc.) and atvise project directories to the exclusion list of the virus scanner.
The export or import time depends on the amount of data. For example, exporting a project with 1 million nodes (nodes.db size of ~500MB) takes around 45 minutes on a standard PC.
If the export or import takes too long, a timeout message is shown and the builder will not wait for the server response anymore. However, the import or export script is still running on the server. Check the server log file ("Finished #<Nr>, duration: <x.y>s") to see when the export or import is completed.
Version control systems must not change the line endings of the exported files and must be configured accordingly.
Checking the server version
A file named "version" is created in the base directory when exporting data. It contains the major and minor version number of the server. This number is checked on every import or export.
If the exported data on the file system is from a newer version, note the following for a subsequent export or import:
Export:
The version number in the "version" file is not changed.
The option delete surplus nodes must not be used. If it is enabled, the export will be aborted.
Import:
Importing data from a newer version is not supported. The import will be aborted.
If the "version" file does not exist or the version number in the file is the same or older, the import or export will run without any restrictions. An export updates the version number in the file.
Export
The whole (selected) address space is mapped to files with an appropriate file structure. A folder is created for every node.
Hint
When mapping nodes to the file system, the BrowseName is used to generate a unique hash value. The respective folder or file name consists of BrowseName and hash value (<BrowseName>_<Hash>). If a BrowseName contains special characters that are not allowed by the file system (\, /, :, *, ?, <, >, |, ', ", blank character), the characters are replaced by an underscore "_".
For each folder, there is at least one meta file <BrowseName>_<Hash>.meta that contains the data necessary for describing the node. Depending on the respective node, the following entries are possible:
NodeId
NodeClass
BrowseName
DisplayName
Description
EventNotifier
Reference
IsAbstract
DataType
ValueRank
AccessLevel
In addition to the meta file, for some nodes there is also an identically named file (.txt for scalar data variables or .xml for scripts, displays and array data variables), that contains the respective value.
Exporting object types and instances
When exporting a type (ObjectType or VariableType) or an instance, all related super types will be completely exported as well (with all child nodes including sub types).
Example:

Instance¶

Types¶
If the instance "Toyota" is exported recursively with dependencies:
Structure of "Toyota" will be fully exported.
Structure of instance type ("car") including sub type "convertible" will be exported.
Structure of super type "vehicle" including sub type "motorbike" will be exported.
Structure of type "tank" ("gas tank" of super type "vehicle") will be exported.
Structure of super type "container" will be exported.
Hint
If the super type is "ObjectTypes.PROJECT", it is not exported.
Import
All (selected) nodes from the file system are imported into the address space. To ensure that no nodes are locked, all opened nodes (displays) should be closed in the builder before the import. Nodes may also be locked by other users or a second opened builder.
Due to dependencies, the import may result in multiple error log entries. E.g.: A node-triggered parameter is defined for a script and the parameter is accessed by the script. If the script is imported and executed before the respective node is imported, the script tries to access a property (= node parameter) that is "null". Thus, a script error is thrown.
If files were changed via the file system, consider the following for correctly importing them:
Directory name and BrowseName must be consistent. Changes to nodes (e.g. bool1 to bool2) must be applied at least to BrowseName in the meta file as well as to the directory name with the hash value. However, we recommend using the same name for the BrowseName and the child BrowseName of the NodeId (see below).
If the data type of a node is changed from an array to a scalar data type, the related XML file that contains the value must be changed to a text file (or vice versa). The file content must be changed according to the type.
If the data type of a node with sub nodes is changed, these nodes are deleted from the address space and created again during the import. In this case, the node values are taken from the file system and not the process image. Since the nodes are newly created, scripts or alarms are triggered after the import.
Hint
Only nodes that exist on the file system are created during the import. Nodes that only existed in the address space will not be recovered in this case.
Changes to types with instances must be applied to the instances as well (and vice versa).
Please note that the user must have sufficient access control rights (= the Engineer right) for every node that shall be imported. Otherwise the complete data cannot be imported which may result in inconsistencies or errors within the project.
Configuration¶
The menu entry allows to set the base directory that defines the starting point for the export and import of the address space. The directory must be located on the computer the atvise server is running on and must be empty or may only contain the default folders (Objects_<hash>, Types_<hash>, Views_<hash>) and the files "Root.meta" and "version" from a previous export. The folder versioncontrol in the project directory is used by default.
Export / Import¶
To export or import the entire project, the following menu entries are available under :
Export Project…
Import Project…
Hint
OPC UA types (namespace 0) as well as atvise-specific types (atvise object types and variable types) cannot be exported.
To export or import specific nodes, select the respective node(s) in the project tree, open the context menu via right mouse click and go to :
Export Node(s)…
Import Node(s)…
Clicking one of these entries opens the following configuration dialog (the dialog for export and import is identically):
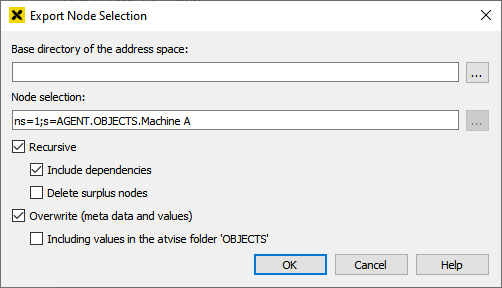
Base directory of the address space – The starting point for the export and import of the address space. If a relative path is defined, it is relative to the project directory.
Node selection – Shows the selected node(s) or the entire project (i=84) that shall be exported/imported.
Hint
The … button is only active if the import configuration dialog is opened for a single element in the project tree. It opens the selector that allows to pick a specific node in the file system. This is necessary if a single node that has already been deleted in the address space shall be imported. Select the respective folder with a double click and confirm with Select. The selected node will be imported into the address space.
Recursive – All child nodes are exported or imported as well. A child node is a node where child NodeID minus child BrowseName corresponds to the parent NodeID (e.g. AGENT.OBJECTS.F1.i16 minus i16 = AGENT.OBJECTS.F1, see picture below).
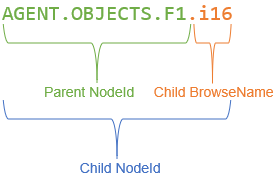
Thus, child nodes are referenced by the selected node with "IsModelParentOf".
Include dependencies – If this option is inactive, only references to non-child nodes are exported or imported. If active, all referenced non-child nodes are exported or imported as well. For example, when exporting/importing object instances, the respective object type is also included. Dependencies within the node content, like linked scripts in object displays, are not considered.
Delete surplus nodes – All surplus child nodes will be deleted.
Export: Child nodes that only exist on the file system, but not in the address space, are deleted.
Import: Child nodes that only exist in the address space, but not on the file system, are deleted.
Hint
This option must be used carefully to avoid deleting nodes accidentally. Example: The folder "Folder1" in the process image contains several nodes and sub folders. Only one single node ("Node1") of the folder is exported. After that, the import is started via the folder's context menu and option delete surplus nodes is enabled, with the exception of "Node1" all other nodes and sub folders are deleted from the address space.
Overwrite (meta data and values) – All target nodes and references (values and meta data) are overwritten by the source.
Including values in the atvise folder 'OBJECTS' – Defines if values of nodes in AGENT.OBJECTS are also overwritten. This option is disabled by default to prevent overwriting current process values or triggering scripts or alarms. The meta data is overwritten in any case.
Example: Node with archive is exported with option include dependencies. The archive is stated as reference in the node's meta file. The corresponding archive group is exported as well. After that, the archive is removed from the node and the node is exported again (with option Overwrite (meta data and values)). The reference to the archive is removed from the node's meta file.
Hint
It depends on the mode which options can be selected:
If you export or import the entire project, only Overwrite (meta data and values) and Delete surplus nodes are editable.
When exporting/importing via context menu, Include dependencies and Delete surplus nodes can only be used in correspondence with Recursive.