Creating a data structure¶
In atvise scada, you are able to create your own data structure in the atvise builder.
The structure of your scada server is located in the Servers ‣ My Server ‣ OBJECTS tree.
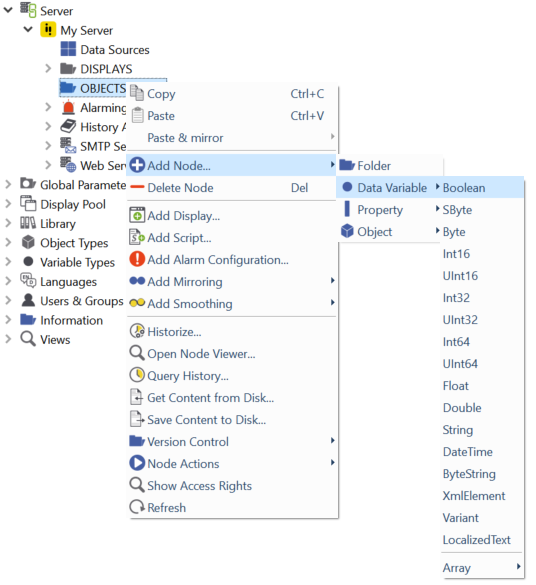
Right-click Servers ‣ My Server ‣ OBJECTS and choose to create folders, data variables, properties and instances of your own object types:
 Folder
Folder
Allows you to add folders to structure your object tree.
 Data Variable
Data Variable
Allows you to add data variables to your object tree.
The following (OPC UA) data types are available :
Boolean |
Boolean resp. bit (true/false). |
SByte |
Signed byte (builder displays decimal value). Range: -128 to 127 inclusive. |
Byte |
Unsigned byte (builder displays decimal value). Range: 0 to 255. |
Int16 |
16-bit integer (signed). Range: -32,768 to 32,767. |
UInt16 |
16-bit integer (unsigned). Range: 0 to 65,535. |
Int32 |
32-bit integer (signed). Range: -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. |
UInt32 |
32-bit integer (unsigned). Range: 0 to 4,294,967,295. |
Int64 |
64-bit integer (signed). Range: -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807. |
UInt64 |
64-bit integer (unsigned). Range: 0 to 18,446,744,073,709,551,615. |
Float |
Defines a value that adheres to the IEEE 754 Single Precision data type definition. |
Double |
Defines a value that adheres to the IEEE 754 Double Precision data type definition. |
String |
Defines a Unicode character string that may not include control characters that are not whitespaces (0x00 - 0x08, 0x0E - 0x1F or 0x7F). |
DateTime |
OPC UA DateTime. Defines a Gregorian calendar date. |
ByteString |
Defines a value that is a sequence of byte values. |
XmlElement |
OPC UA XmlElement. |
Variant |
Defines a value without a specific data type. The value of such a variable can only be set within a server side script. |
Array |
Allows you to add an array of the described data types. |
Adding a data variable¶
 Property
Property
Basically, a property is the same as a data variable (for a description, see section above). The only relevant difference is that a property must always be a leaf in the object tree (so it can have no child nodes).
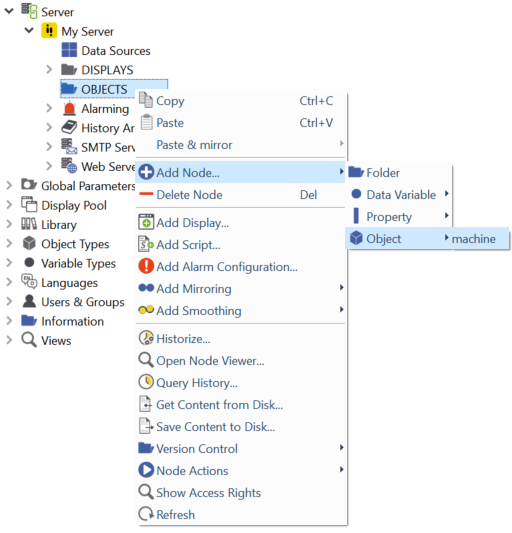
 Object
Object
Allows you to add instances of your own object types to your project's data structure.
To add an object instance, choose .
Adding an object instance¶
Now the "Create Object Instance(s)" window appears and you can choose from 3 possibilities of how to create instances:
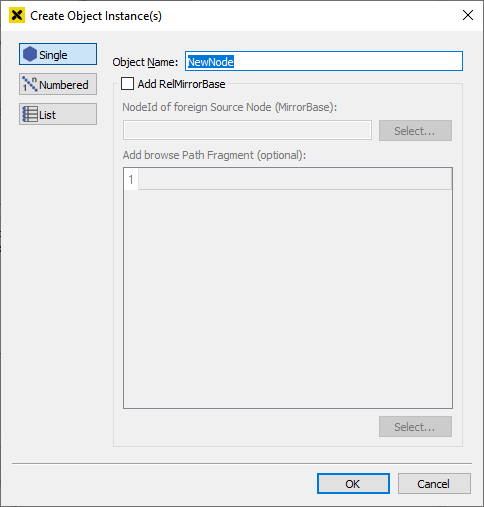
Single
Creates a single object instance. You only have to key in the name of the object you want to add and then click OK.
You can directly add a "RelMirrorBase" to the object instance - go to the section Object oriented - relative mirroring for a detailed explanation.
Creating a single object instance¶
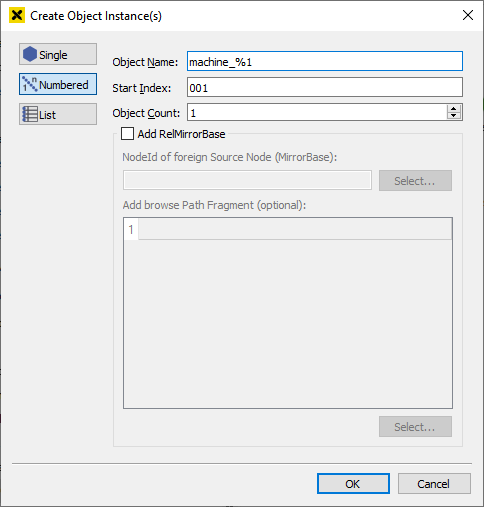
Numbered
If you want to add several consecutively numbered object instances, choose "Numbered". Here you put in an object name, a start index for your numbering and the number of object instances you want to create.
Use %1 as a wild card for your numeration.
For example: LightObject_%1 will be LightObject_001, LightObject_002, … after being added.
You can directly add a "RelMirrorBase" to the object instances - go to the section Object oriented - relative mirroring for a detailed explanation.
Creating several consecutively numbered object instances¶
List
If you click on list, you can import a CSV file for your object instances.
The list contains a locale name and a corresponding browse name for the data source (to add a relative mirror base to the instances - see Object oriented - relative mirroring)
Syntax for the "Source Browse Name": [namespace]:[browse name]
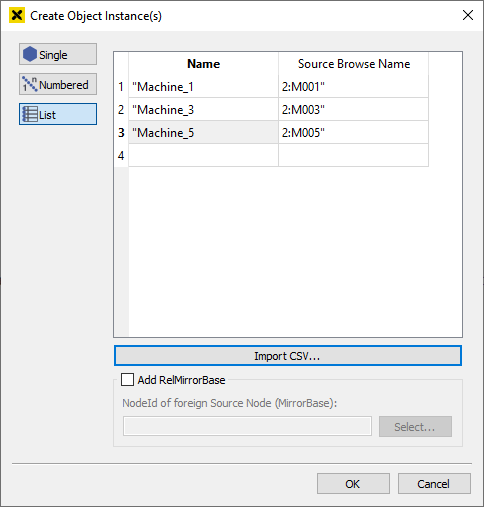
Creating several object instances from a CSV file¶