Mirror variables from data sources¶
Basics
This section describes how to mirror variables from a defined data source into the atvise data structure ("MirrorInput") and how to mirror atvise variables to a variable of a defined data source ("MirrorOutput").

"MirrorInput" and "MirrorOutput"¶
Basically, there are two ways to create mirrored data variables in the atvise builder:
Attention
If you have problems with the connection to a OPC DCOM server, please check out the OPC COM configuration page.
Hint
When browsing the TwinCAT DCOM server an object instance can be found as a byte string variable without any sub-node and additionally as a folder with the same name, which includes all sub-nodes. Even so the byte string variable might appear first in the list and the folder further down, for the mirroring of the sub-elements only the folder can be used and the byte string variable has to be ignored.
MirrorInput
A local data variable with a "MirrorInput" property will automatically receive the current data values of the foreign data variable which is defined in this "MirrorInput" property.
Hint
If the connection to the data source from which the variable is mirrored breaks down, the status of the local value will change to "BadNotConnected".
When the data source is reconnected, the state of the value will switch back to "Good" and the current value of the foreign variable will once again be input mirrored.
MirrorOutput
All data values set to a local data variable with a "MirrorOutput" property will be written to the foreign data variable which is defined in this "MirrorOutput" property.
Hint
If the connection to the data source to which the variable is mirrored breaks down, the status of the local value will change to "BadNotConnected".
When the data source is reconnected, the state of the value will switch back to "Good" but the current local value will not be written to the data source (the current value on the data source - usually a PLC - has higher priority and will not be overwritten).
MirrorInputOutput
MirrorInputOutput is a combination of MirrorInput and MirrorOutput.
MirrorDisable
With MirrorDisable you can disable communication with a data source for a single variable or a sub-tree. All MirrorInput, MirrorOutput and MirrorInputOutput that exist below the node, where MirrorDisable was created, will be ignored, if MirrorDisable is set to "true".
Hint
If a variable should be communicated despite MirrorDisable, you can create a boolean property with the name "Permanent" and the value "true" at the respective MirrorInput (or MirrorOutput, MirrorInputOutput as well as RelMirrorInput etc.). For such a variable MirrorDisable will have no effect.
RelMirrorDisable
With RelMirrorDisable you can disable the creation of mirroring nodes for a single variable or a sub-tree.
All RelMirrorInput, RelMirrorOutput and RelMirrorInputOutput that exist below the node, where RelMirrorDisable was created, will be ignored, if RelMirrorDisable is set to "true". If RelMirrorDisable is set to "false" then the subtree is enabled again.
RelMirrorDisable can be embedded into a subtree of other RelMirrorDisable. The RelMirrorDisable nodes of a subtree will be evaluated in top-down order and the last found value will be used.
RelMirrorDisable is different from MirrorDisable. RelMirrorDisable influences the creataion of mirror nodes. MirrorDisable influences the communication between mirrored nodes and data sources.
Hint
If mirroring nodes of a variable should be created despite RelMirrorDisable, you can create a boolean property with the name "Permanent" and the value "true" at the respective RelMirrorInput (or RelMirrorOutput, RelMirrorInputOutput). For such a variable RelMirrorDisable will have no effect. The "Permanent" property will be copied to mirroring nodes.
MirrorOnDemand
With "MirrorOnDemand" a variable with a "MirrorInput" or "MirrorInputOutput" will only be updated with values from the data source when the variable is subscribed from a currently opened display in a browser. If the variable is not subscribed at least once, the value will not be updated and the status of the variable is set to UncertainLastUsableValue.
To add "MirrorOnDemand" to a variable, right-click the desired variable and choose from the context menu. A variable with the name "MirrorOnDemand" will be created below the desired variable.
To disable "MirrorOnDemand", remove the variable "MirrorOnDemand" or set its value to "false".
Attention
Be aware that – with "MirrorOnDemand" enabled – historization, alarming, scripts etc. will only work when the respective variable is currently subscribed in a display.
Smoothing
Smoothing allows to limit the number of value changes written to a data variable. Smoothing can be applied to any data variable, but it is mostly used at mirrored variables. It´s possible to use multiple smoothing properties per variable. Status changes of the variable are always applied independently from the smoothing.
The following smoothing properties are available:
Change Comparison – If you add a "Change Comparsion" property to a mirrored data variable it has to activated and a new value will only be set on the mirrored data variable if it differs from the current value or if the status changes.
Deadband Absolute – You can set an absolute value to this property; a new value will only be set if the value has changed by at least this deadband value. (e.g. if you have a DeadbandAbsolute with a value of 0.1, the new value has to change at least by 0.1 to be set).
Deadband Relative – Similar to deadband absolute, but with a percentage value. (e.g. if you have a DeadbandRelative with value 10, the new value has to change at least by 10% to be set).
SuppressFlicker – Enter a time in milliseconds. The timestamp of a new value has to differ by at least this time from the timestamp of the current value to be set.
To add smoothing, right-click a mirrored data variable and choose Add Smoothing from the menu:
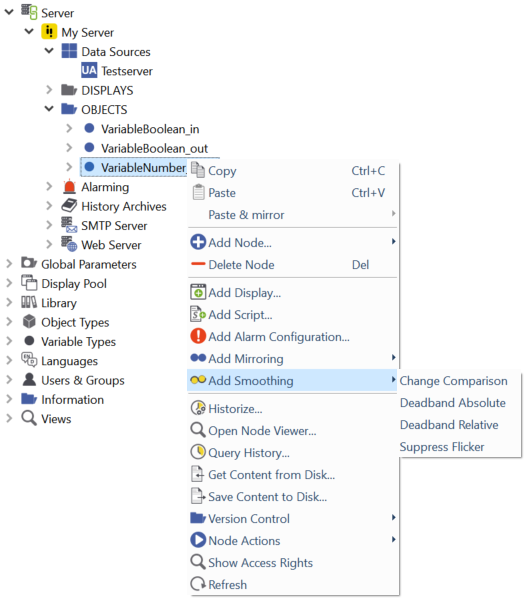
Add smoothing to a mirrored data variable¶
Linear Conversion
By means of linear conversion the mirrored input/output value in atvise can be converted after received from or before sent to the data source.
Right-click on the mirroring of a node.
Choose
Two properties will be added to the mirroring. "LinearConversionSlope" and "LinearConversionYIntercept".
Double-click these properties to change their values.
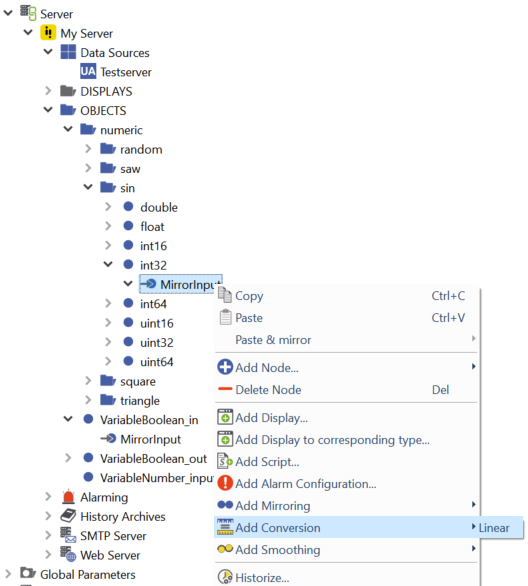
Adding a linear conversion¶
The conversion is a simple linear function defined by
y = k * x + d, where
x denotes the value stored in the data source
y denotes the mirrored value stored in atvise
k defines the slope of the linear conversion denoted by the property name "LinearConversionSlope"
d defines the offset of y if x = 0 denoted by the property name "LinearConversionYIntercept" as can be seen on the next figure:
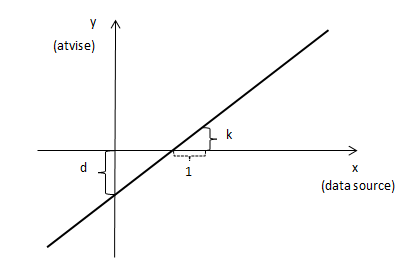
Example:
The valuerange of a node in the data source is between 0 and 100.
It should be converted to a mirrored node in atvise in the range between -5 and 5.
Set LinearConversionSlope to 0.1
and LinearConversionYIntercept to -5
Now the range of the value will be converted to the desired range.
Hint
Linear conversion can be configured on MirrorInput, MirrorOutput, MirrorInputOutput and their relative mirroring counterparts RelMirrorInput, RelMirrorOutput, RelMirrorInputOutput.
In input direction, the conversion function will be applied directly.
In output direction, the inverse of the conversion function will be applied. The result of the calculation is always of data type "double", therefore the value can only be written if it is also of data type "double" at the data source!